Assessing vulnerability
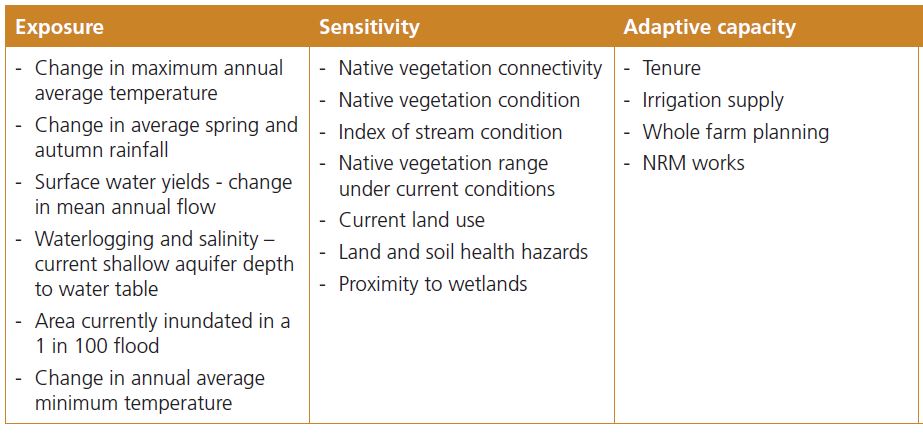
Vulnerability is the degree to which a system is susceptible to, and unable to cope with, adverse effects of climate change. It has three main dimensions: exposure to changes in climate; sensitivity to such changes; and the capacity of a system to adapt to them. See figure below.

Figure: Vulnerability assessment approach
An assessment of the vulnerability of the Goulburn Broken Catchment’s natural resources to climate change has been undertaken using three climate change scenarios :
- 2030 – Low change: warmer (0.5-1.5°C increase in annual average temperature), with little change in annual average rainfall (-5 to +5% change).
- 2050 – Moderate change: hotter (1.5-3.0°C increase in annual average temperature) and drier (5-15% reduction in annual average rainfall)
- 2070 – High change: High climate change: much hotter (>3.0°C increase in annual average temperature) and much drier (>15% reduction in annual average rainfall)
Table: Criteria used for assessing vulnerability